Cybercrime incidents are growing worldwide with each passing year. An alarming picture is painted by the cyberattacks’ increasing frequency and size. To name a few significant factors contributing to this expanding trend among many others: nation states are becoming an ever-increasing factor to consider, organizations are not implementing adequate cybersecurity measures, hackers are using more sophisticated tools, and techniques, and more serious cyber threats are emerging every day.
In a time when digital technologies are enabling modern businesses at every level, enterprise cybersecurity is an essential requirement. Due to growing awareness and stringent regulations, businesses everywhere are taking a number of measures to protect their infrastructure and data. No cybersecurity program, however, is completely impenetrable. As a result, creating an incident response plan is crucial, and its benefits must be taken into account.
The NIST incident response framework aims to help organizations improve their security posture and incident response capabilities via proper planning, cybersecurity training, and resource allocation. In this article, we will discuss what NIST is, its incidence response framework, its benefits, and how it compares with SANS incident response framework while also providing answers to frequently asked questions.
What Is NIST Incident Response Plan?
NIST Incident Response Plan is a set of guidelines and procedures developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to help organizations respond to cyber security incidents.The actionable steps for identifying, containing, eliminating, and recovering from a security incident are described in the plan. Additionally, it offers instructions on how to set up an incident response team, formulate an incident response plan, specify incident response procedures, and develop an incident response policy.
The NIST Incident Response Plan is designed to help organizations prepare for and respond to cyber security incidents in an effective and efficient manner. It offers instructions on the steps that should be taken to ensure the security of an organization’s data and IT systems.
This entails spotting and countering potential threats, stopping the incident in its tracks and cleaning it up, as well as recovering from the incident. Additionally, the plan specifies the obligations of the incident response team and offers instructions on how to draft an incident response policy.
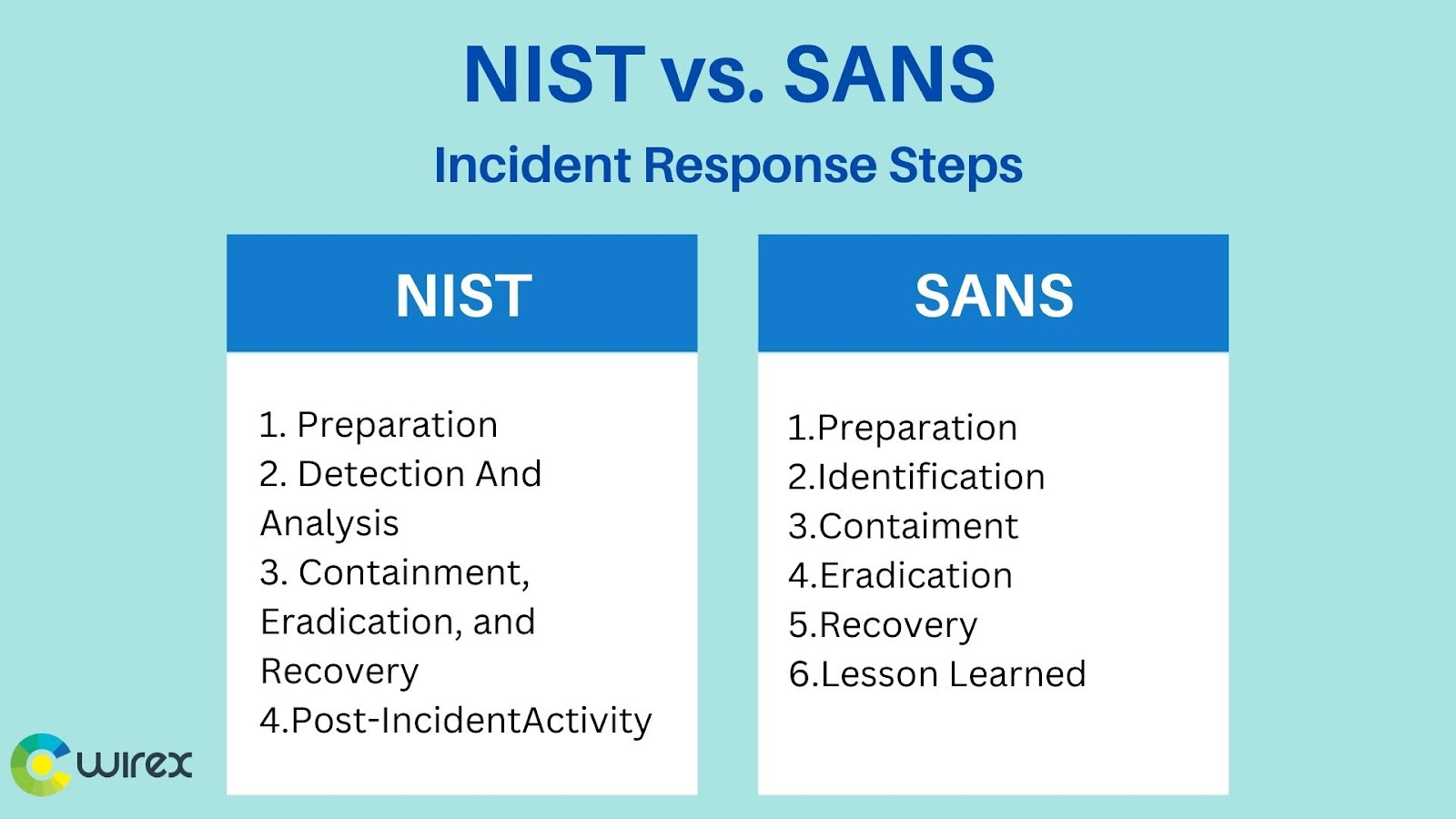
NIST vs. SANS
Two of the most well-known companies in the cybersecurity industry are the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the SANS Institute. Both organizations offer advice and resources on various security-related subjects, such as incident response. But there are some significant distinctions between the two organizations’ approaches to incident response.
The NIST Computer Security Incident Handling Guide is a comprehensive set of guidelines provided by NIST for incident response (NIST SP 800-61). This manual offers comprehensive instructions on how to respond to security incidents, from planning to follow-up actions. It addresses issues like incident classification, containment, elimination, and recovery.
The SANS Institute, in contrast, offers a more all-encompassing method of incident response. Instead of offering in-depth technical advice, the incident response guide from the SANS Institute concentrates on the process of responding to an incident.
It addresses issues like planning, preparing, and carrying out incident responses. It also offers instructions on how to set up an incident response team and a policy for responding to incidents.
Overall, incident response best practices are offered by both NIST and SANS. They do, however, approach incident response in very different ways. While SANS offers more general advice on the procedure for responding to an incident, NIST offers detailed technical guidance on how to handle security incidents.
Why You Need An Incident Response Plan
The definition of a breach, the roles and responsibilities of the security team, the tools for managing a breach, the steps that must be taken to address a security incident, how the incident will be investigated and communicated, and the notification obligations following a data breach are all laid out in incident response strategies and plans.
Below are the reasons you need an incident response plan.
Protect Your Data
Data security is crucial for both personal and professional reasons. By following an updated incident response plan, your team can contribute to the prevention of data loss. Data in the wrong hands means the consequences could be disastrous when a hacker uses ransomware (WannaCry, Petya, NotPetya, etc.) or when private information is made available to the general public.
Protecting data assets during the incident response process involves a variety of tasks and responsibilities for the IR team. To prevent insider threats, it’s essential to perform secure backups, monitor logs, and security alerts for suspicious activity, manage identities and access appropriately, and apply patches carefully.
Build Trust
Customers, business partners, and other stakeholders favor businesses with effective incident response plans. These types of proactive measures demonstrate that a business has worked to strengthen its incident response capabilities.
Most Fortune 500 companies have experienced a cyberattack at some point or another. In the face of the difficult cybersecurity environment, an incident response plan significantly helps to build trust among an organization’s stakeholders and helps to preserve the evidence necessary for root cause analysis and prosecution.
It Gives You An Organized Approach
Security incidents are nearly impossible to predict. Even if it seems like they are well protected, any organization can be caught off guard by unplanned incidents. By proactively implementing an incident response plan, you can rely on having a precise, methodical plan of action to follow in urgent situations.
Even if a company is prepared for a cyberattack, it may not be able to defend itself if the team is in panic and unprepared to handle it. An incident response plan helps to systematically secure the entire organization, address vulnerabilities, and lessen the impact of an attack.
Additionally, it ensures that the company can use its staff, tools, and resources wisely to deal with the issue and lessen the impact it has on other operations. The overall cost and response time are both reduced with an incident response plan.

Why Is It Important?
The NIST Incident Response Plan is an important tool for businesses of all sizes to protect their networks, systems, and data from cyber-attacks. It provides guidance on how to respond to a cyber incident in a timely and effective manner. The response plan outlines the steps to be taken to investigate, contain, and remediate the incident, as well as how to report the incident to the appropriate authorities.
The plan also outlines how to respond to a potential data breach and how to ensure that the incident is properly investigated and that the data is recovered. By following the NIST guidelines, businesses can ensure that their networks, systems, and data are more secure and that their response to a cyber incident is effective.
NIST Incident Response Plan Benefits
Helps your organization achieve a global standard of cybersecurity
The NIST Framework includes knowledge from numerous information security specialists from around the world. Since it is regarded as an industry best practice and has the most comprehensive set of controls of any framework, it enables your organization to address the majority of cybersecurity blind spots it might have overlooked.
Enables faster business growth
Whether your organization has adopted the NIST Framework or not can instantly make or break relationships with clients, partners, and vendors. Implementing a standard like NIST enables your business to develop more successfully with supply chains, which promotes faster business growth. Security online is quickly emerging as a major selling point.
Built for all of your stakeholders
The NIST Framework is created in a way that allows all stakeholders — technical as well as non-technical — to comprehend the advantages of the standard. It is simple for your technical staff to understand the advantages of enhancing the company’s security, and it is also simple for the executives because the framework adopts a risk management approach that is well-aligned with your organization’s goals.
Adopting the NIST Framework facilitates decision-making across your organization, improves communication, and makes budgeting for security efforts easier to justify.
Flexible and easily adaptable regardless of the size and type of your business
Because it is designed to be a risk-based, outcome-driven approach to cybersecurity, the NIST Framework is very adaptable. The NIST framework is readily adopted by small and medium-sized businesses as well as critical infrastructure companies in the energy and finance sectors due to its voluntary nature, which makes it simple to customize to your business’s unique cybersecurity needs.
The Core Functions, Implementation Tiers, and Profiles can provide businesses with the guidance they need to create a cybersecurity posture that complies with global standards.
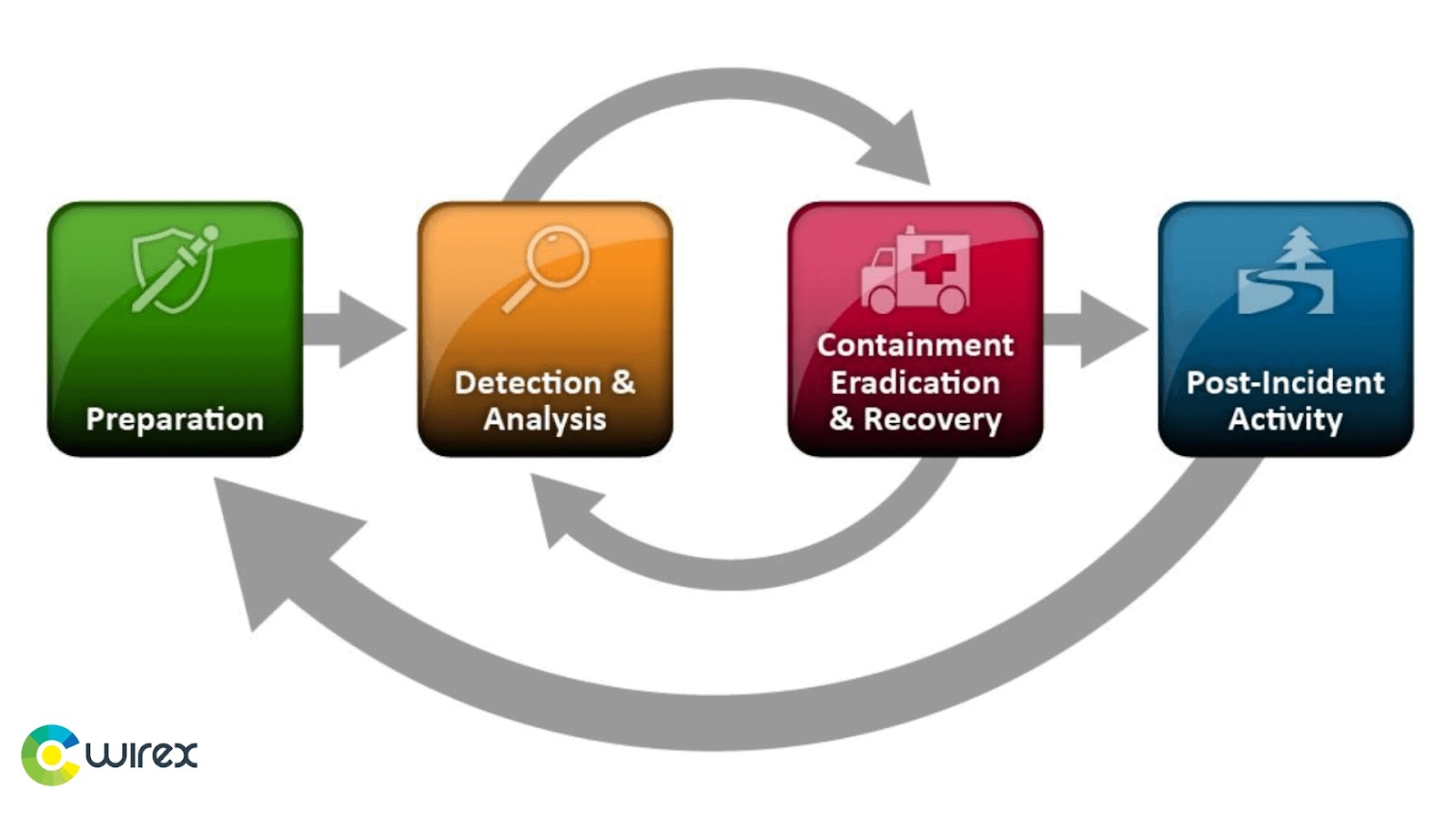
NIST Incident Response Plan Steps
The NIST Incident Response Plan Steps provide a comprehensive guide for businesses to respond to cyber security incidents. The steps are divided into four main categories: Preparation, Containment, Eradication, and Recovery.
Preparation
The NIST Incident Response Plan begins with preparation. It entails determining the resources that will be required and evaluating the organization’s readiness to respond to a cybersecurity incident. To respond to the incident, it is necessary to decide who will be involved, what equipment will be used, and what procedures will be followed.
It is important to make sure that the organization has the personnel and resources needed to handle an incident. This includes personnel with the necessary technical knowledge as well as personnel with the required interpersonal and managerial abilities.
In order to respond to an incident, the organization should also have the required resources and procedures in place. This includes methods for reporting incidents to the appropriate authorities as well as tools for locating, evaluating, and responding to incidents.
Detection and Analysis
Before proceeding to the detection and analysis stage, it is necessary to ascertain the kind of threat you are dealing with. NIST provides a list of potential threat categories along with a division into two groups of incident precursors and indicators.
Both precursors and indicators suggest potential future, current, and past incidents, as well as potential current and past incidents, respectively.
Unfortunately, most attack warning signs only surface once the attack has already begun. However, a business with a strong incident response capability may be able to recognize warning signs and prevent an attack before it even begins or early enough to prevent breach from growing into larger problem.
Containment, Eradication & Recovery
Containment, eradication, and recovery are the three main elements of the active incident response. At this stage of the incident response process, the threat must be isolated to stop it from spreading. The containment strategy must, however, be appropriate for the type of attack and the potential harm that a continued attack could cause, according to the NIST documentation.
According to several risk assessments and analyses, NIST advises that the incident response team have a specific containment plan for each type of attack they expect because simply cutting off the attacking host from the data source could have unintended consequences.
Post-Incident Activity
The team should hold a “lessons learned” meeting to process the incident, discuss methods for preserving the data and evidence gathered throughout the meeting, and review preparation for anticipated future cybersecurity threats, according to NIST, which claims that this step is both the most frequently skipped and the most crucial. Making a follow-up report on every aspect of the incident is another task included in this phase.
This report can be used both internally and shared with external organizations because managing and preventing cybersecurity threats frequently requires collaboration and mutual involvement throughout the entire incident response cycle.
How To Organize Incident Response Plan
Establish An Incident Response Team
Any organization’s security strategy should include the creation of an Incident Response Team (IRT). An IRT is a team of people in charge of managing and responding to security incidents.
A critical aspect of any organization’s security plan should be the creation of an incident response team (IRT). An IRT is a team of people in charge of handling security incident response and management. Members of the team should come from various departments, including IT, legal, human resources, and others. This guarantees that the team can respond to incidents in a timely and efficient manner.
Create An Incident Response Policy
One of the most important steps in preparing your organization for a cyber incident is developing an incident response policy. The steps that will be taken in the event of a security breach or other cyber incident are described in an incident response policy. It offers instructions on how to handle a cyber incident and best safeguard the organization’s data, systems, and networks.
The entire incident response process, from initial detection to post-incident activity, should be covered by the policy. The roles and responsibilities of the incident response team, the kinds of incidents that should be reported, and the procedures to be followed in order to contain, eliminate, and recover from an incident should all be covered. It should also contain information on how to report an incident, and to what extent to involve outside agencies like law enforcement and third-party vendors.
Define An Incident Response Plan
An Incident Response Plan is a set of procedures and processes that organizations use to respond to and manage incidents. It is a critical component of an organization’s security posture and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
A response plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to respond to an incident. It should include the roles and responsibilities of each team member, the processes to be followed, and the tools to be used. It should also include information on the types of incidents that are covered, the reporting process, and the communication plan.
The NIST Incident Response Plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the steps that need to be taken in order to respond to an incident. It is based on the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and covers a wide range of incident response topics, including:
- Establishing an incident response team
- Identification of an incident
- Containment, eradication, and recovery
- Communication and reporting
- Organizing incident response
- Post-incident activity
The NIST IRP provides organizations with a comprehensive set of procedures and processes to help them respond to incidents quickly and effectively. It is an important part of any organization’s security posture and should be tailored to the organization’s specific needs.
Final Thoughts
NIST’s incident response strategies and their vision for the incident response cycle are some of the best options available for IT management teams and CIOs looking to protect their business from costly, reputation-damaging cybersecurity events and figure out how to prevent cybersecurity breaches.
Although we may not be able to completely prevent incidents, NIST acknowledges that we can definitely lessen the negative effects they have on our businesses and personal lives. In the world of IT, incidents are a given. As a result, merely adhering to the framework is insufficient. You should put systems in place for threat detection and reaction.
The threat detection and response platform from WireX Systems engages your entire security team in conducting investigations significantly more quickly and effectively while providing visibility that goes far beyond EDR and SIEM logs.
Powered by Contextual CaptureTM Technology, the solutions continuously monitor the entire enterprise network stack and translate it into content and behavior-aware intelligence for immediate use, delivering months of in-depth visibility.
Are you looking to find out what threat detection and response platforms work for your business, or do you want to improve on what you already have?
Reach out to us today to maximize your security operations ROI.
FAQs
What’s the difference between NIST and SANS?
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) is a government agency that sets standards for cybersecurity, including incident response plans. SANS (SysAdmin, Audit, Network, Security) is a cybersecurity organization that provides training and certification for IT professionals.
While both organizations provide guidance on incident response, NIST is the official standard for the US government and is the basis for many organizations’ incident response plans.
Does it provide a recommended checklist of what all organizations should do?
No, the Framework provides a series of outcomes to address cybersecurity risks; it does not specify the actions to take to meet the outcomes. Because standards, technologies, risks, and business requirements vary by organization, the Framework should be customized by different sectors and individual organizations to best suit their risks, situations, and needs.
Organizations have unique risks – different threats, different vulnerabilities, different risk tolerances – and how they implement the practices in the Framework to achieve positive outcomes will vary.
Where can I get the NIST guidelines?
NIST provides a variety of documents and guidelines related to incident response. The most comprehensive document is NIST Special Publication 800-61, which outlines the Incident Response Process. This document is available on the NIST website, as well as other sources.
What is the difference between NIST 800-37 and NIST 800-53?
NIST 800-37 is the Risk Management Framework for Information Systems and Organizations and provides guidance on how to manage security risks. NIST 800-53 outlines the security controls that organizations should implement to protect their systems. Both documents are important components of any incident response plan.
What is the Framework Core, and how is it used?
The Framework Core is a collection of cybersecurity tasks, ideal results, and relevant resources that are utilized by all critical infrastructure sectors. The phrase “physical devices and systems within the organization are inventoried” is an example of Framework outcome language.
The Core presents industry norms, regulations, and best practices in a way that enables cross-organizational communication of cybersecurity initiatives and results from the executive to the implementation/operations levels.






