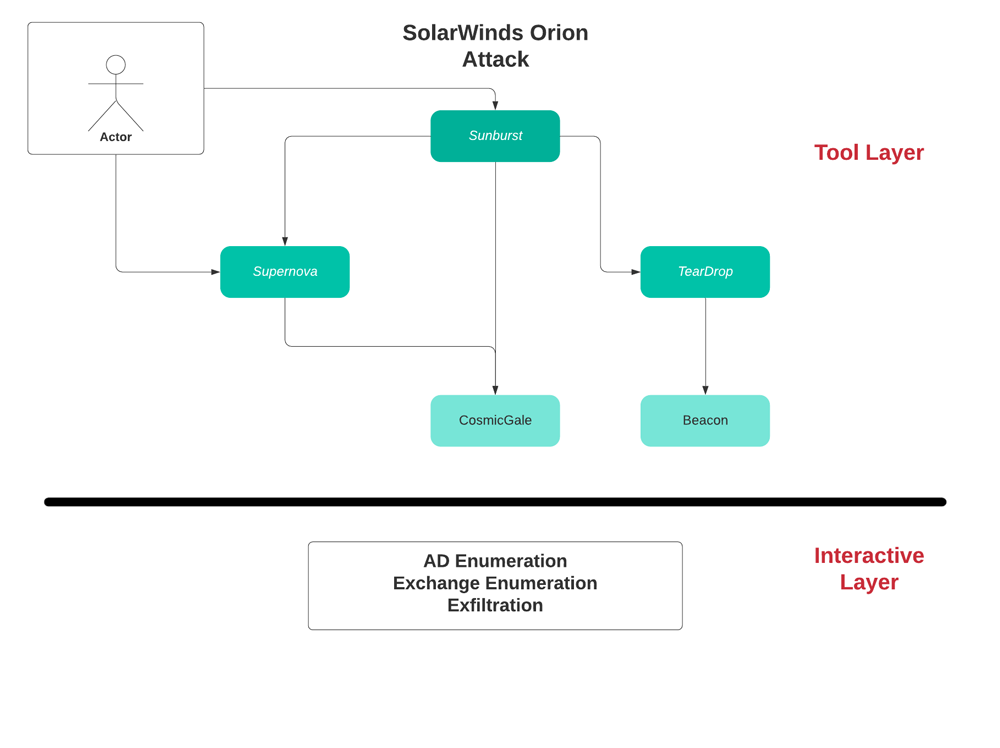
Sunburst – overview
This is the first stage backdoor installed on the victim’s solarwinds Orion server. It is digitally signed & downloaded as a package update from the compromised solarwinds update server.
Sunburst is a first stage backdoor used to evaluate the victim’s environment in order to decide if the victim is interesting for further exploitation.
Sunburst lies dormant for 12-14 days (configurable) & when it runs it performs a check for security tools running on the computer from opsec perspectives.
Sunburst hides its communication as a legitimized solarwinds Orion communication protocol called OIP. While communicating with a C2 coordinator using DNS protocol to stay stealthy from network detection.
Sunburst also uses local solarwinds configuration files in order to hide its configuration variables.
- Type: Implant/Backdoor
- Filename: Solarwinds.orion.core.businesslayer.dll
- Signed: yes
- Installation type: remote, compromised on update/install
- Init: 12-14 days after installation (configurable)
- Persistence: by solarwinds service
- Abilities:
- File xfer
- File execution
- System profiling
- Reboot
- Disable service
- Communication: OIP protocol (SW HTTP API) + DNS
- Storage: plugin config (solarwinds)
- Main C2: avsvmcloud.com
- Opsec:
- Check if in victim’s domain
- Check blacklisted services
- Disable blacklisted services
- Encode dns queries to C2
- Check for internet connection to SW domain
- Check CIDR range
- C2 DNS coordinator
- Driver query (WMI)
- Named pipe (only 1 instance)
- Steganography, Encoding
- Installation: MSP file
- Vector: DLL
- Language: .NET
- Invoke: Inventory manager plugin of SW
Sunburst – Detection
- New upload paths to server (C2)
- DNS:
- DNS bursts to same domain (X in X minutes)
- # of DNS queries to server
- DNS queries return different IP’s
- 5 Levels domain name
- Query length
- New connection to unknown domains
- SW activity to domains not related to SW
- SW UA reaching domains different than SW
- Upload rate/size
- Active scans: C2 RDP response with victim’s hostname
Supernova – overview
Supernova is a dynamically compiled Web Shell which runs in memory, it is a piece of code injected into a legit solarwinds server side file which its original purpose is to return a logo of a network device to agents. The attacker added 4 new get parameters to the file which allows them to dynamically run C# code on the victim host. Since it runs in memory only, dynamically compiled & runs legit C# code it will evade any file system scanner such as AV software.
- Type: Dynamically compiled web shell
- Filename: app_web_logoimagehandler.ashx.dll
- Invoke: added 4 new parameters to API
- Persistence: compiles in memory on the fly
- Signed: NO
- Init: implanted API runs C# code from C2 on the fly in memory
- Parameters:
- Clazz – C# object name
- Method – method to invoke
- Args – arguments to method
- Codes – namespace/assembly/Code to compile
Supernova – Detection
New GET parameters in API
- Method allows upload of files (instead of statically returning logo.gif)
- API requests from non-Orion servers/outside the corporate
- API returns plain text http header in reply (text/plain) instead of (image/gif)
TearDrop – overview
TearDrop is a memory only dropper which drops CobaltStrike beacon disguised as a JPG file.
- Type: memory dropper
- Init: Service
- Config: gracious_truth.jpg (fake header, probably beacon)
- Usage: drop beacon
- File: netsetupsvc.dll
- InstalledBy: Sunburst backdoor()
CosmicGale – overview
CosmicGale is credential theft & reconnaissance PowerShell script intended to harvest credentials & encrypt the results on a local file
- Type: Credential Theft & Reconnaissance
- Vector: PS script
- Actions:
- Get credentials using get-pass-hashes script
- Clear log files
- Write data to encrypted file
Interactive activity – overview
- Reconnaissance:
- GetUserList & Role from exchange server
- Get info on virtual directories on exchange servers
- Get info from AD using ADFIND
- Lateral MVMT:
- Schtasks on remote machines (RPC/DCOM)
- SMB shares
- WMI actions
- Exfiltration:
- Through local folders using tools
- Remotely through HTTP root directories on Exchange server (OWA)
- Through email exfiltration
Interactive activity – detection
- NTLM authentications from different users on remote machines
- SMB read/write/delete file on remote machines
- DCE-RPC binds
- Multiple usage of credentials to target/s (SMB/AD)
- Multiple usage of credentials in small time frame
- Direct file download from Exchange server on HTTP root/special folders
- Increase in number of hosts logged into
- First time logon to a server from a user
- Remote WMI over RPC
- New RDP connections
- Increase in total number of RDP connection in network
- Increase in interactive logons
- New user email accounts
- File header different from file extension (for toolset)
- User account used from remote geo-locations
- Many logins from server outside the network (1 to many)
- SMB file manipulation in short amount of time
- Increase in number of SCHTASKS
- C2 hostname = victim’s hostname




